1514. Path with Maximum Probability
#Algorithm #Algorithm_Dijkstra #Algorithm_Graph #DataStructure-Priority_Queue #DataStructure-Heap
1514. Path with Maximum Probability
1. 문제
1-1. 원문
You are given an undirected weighted graph of n nodes (0-indexed), represented by an edge list where edges[i] = [a, b] is an undirected edge connecting the nodes a and b with a probability of success of traversing that edge succProb[i].
Given two nodes start and end, find the path with the maximum probability of success to go from start to end and return its success probability.
If there is no path from start to end, return 0. Your answer will be accepted if it differs from the correct answer by at most 1e-5.
Example 1:
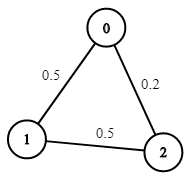
Input: n = 3, edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[0,2]], succProb = [0.5,0.5,0.2], start = 0, end = 2
Output: 0.25000
Explanation: There are two paths from start to end, one having a probability of success = 0.2 and the other has 0.5 * 0.5 = 0.25.
Example 2:
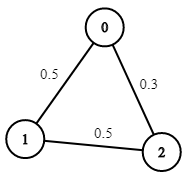
Input: n = 3, edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[0,2]], succProb = [0.5,0.5,0.3], start = 0, end = 2
Output: 0.30000
Example 3:
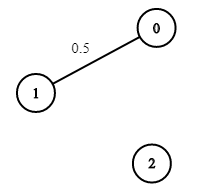
Input: n = 3, edges = [[0,1]], succProb = [0.5], start = 0, end = 2
Output: 0.00000
Explanation: There is no path between 0 and 2.
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 10^40 <= start, end < nstart != end0 <= a, b < na != b0 <= succProb.length == edges.length <= 2*10^40 <= succProb[i] <= 1- There is at most one edge between every two nodes.
1-2. 내용 번역
n개의 노드를 가진 무향 그래프가 주어진다. 각 노드 사이의 엣지의 가중치는 edges와 succProb 배열을 가지고 알 수 있다. edges[i]는 2개의 요소를 가진 배열을 나타내는데 [a, b] 노드a와 노드b가 연결되어 있다는 것을 의미하고, succProb[i]는 노드a와 노드b를 연결하는 엣지의 가중치를 의미한다. start 노드에서 end 노드까지 이동한다고 할 때 가중치가 최대가 되는 이동경로의 값을 구하여라.
2. 문제 이해
2-1. 내용 이해
Example1을 보면 노드0에서 노드2까지 가는 경로의 가중치중에 가장 큰 가중치를 구하면 된다. 우선 0에서 2까지 가는 경로는 0->1->2, 0->2가 있다. 그리고 각각의 가중치는 0.5*0.5, 0.2 이므로, 0->1->2 경로의 가중치 0.25가 최대의 가중치가 된다.
2-2. 접근법 생각
경로의 가중치? 비용? 다익스트라.
2-3. 적용한 풀이
Dijkstra
이 문제에서 주목해야 할 것은 가중치를 서로 곱하여 계산한다는 것이다. 소소한 변형이지만, 이것때문에 최초 시작 노드의 시작 가중치가 0이 아닌 1이 되어야 한다는 차이도 발생시키므로 주의해야 한다.
그리고 이 문제는 종료 노드가 있기 때문에 모든 노드의 값을 배열에 저장하지 않아도 되며(큐에 갱신된 값이 저장되기 때문에) 종료 노드를 만나는 즉시 결과 값을 리턴할 수 있게 된다.
3. 구현
class Solution {
fun maxProbability(n: Int, edges: Array<IntArray>, succProb: DoubleArray, start_node: Int, end_node: Int): Double {
val graphMap: MutableMap<Int, MutableSet<ConnInfo>> = mutableMapOf()
val visitedEdges: MutableSet<Int> = mutableSetOf()
val pq: PriorityQueue<ConnInfo> = PriorityQueue {o1, o2 -> if (o1.prob < o2.prob) 1 else -1} // 내림차순 정렬
for((idx, edge) in edges.withIndex()) {
// 무향 그래프
(graphMap.getOrPut(edge[0]){mutableSetOf()}).add(ConnInfo(edge[1], succProb[idx]))
(graphMap.getOrPut(edge[1]){mutableSetOf()}).add(ConnInfo(edge[0], succProb[idx]))
}
pq.offer(ConnInfo(start_node, 1.0)) // 가중치 1에서 시작
while(pq.isNotEmpty()) {
val curNode = pq.poll()
val curNodeProb = curNode.prob
if (curNode.edge == end_node) return curNodeProb
visitedEdges.add(curNode.edge)
graphMap.getOrDefault(curNode.edge, mutableSetOf()).forEach { (edge, prob) ->
if (!visitedEdges.contains(edge)) {
pq.offer(ConnInfo(edge, curNodeProb*prob)) // 갱신된 노드의 가중치가 큐에 저장되기 때문에 별도의 배열 없이 계산 가능
}
}
}
return 0.0
}
}
data class ConnInfo(val edge: Int, val prob: Double)